Ruthenium
Ruthenium (Ru) is one of the platinum-group metals (PGMs). It is a shiny, hard, silvery-grey and polyvalent element with a very high melting point. The metal generally occurs in orebodies along with the other PGMs and is widely used in industrial applications, particularly in electrical end-uses, as a chemical catalyst and in electrochemical processes.

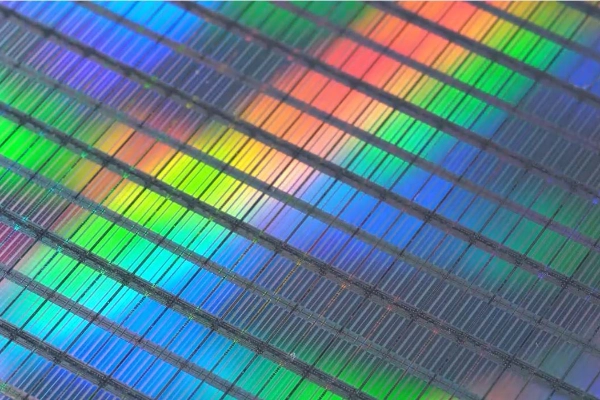
Ruthenium is one of the most effective hardeners for platinum and palladium and is alloyed with these metals when producing electrical contacts to ensure a high degree of wear resistance. These are only a few of the many applications in which ruthenium is used, and new uses of ruthenium are being researched. Heraeus also offers different volatile ruthenium precursors for use in the semiconductor industry. Especially in small-scale architectures, circuitry made of ruthenium exhibits unique material properties.
Ruthenium shares some of the same properties – catalytic, electronic and thermal/chemical resistance – of the other PGMs, so is frequently used in combination. When there is flexibility on how to achieve the required performance and durability, it is often attractive to increase the ruthenium content, particularly compared to iridium, given ruthenium mine production is around four times higher than iridium and its price is historically substantially lower.
Thanks to the extensive experience in the processing of precious metals, Heraeus also offers the recovery of materials containing ruthenium. Depending on whether it is pure ruthenium or ruthenium alloys, the used ruthenium from products and applications can be recovered through melting or precious metal recycling.
For detailed information on the aforementioned products and applications involving ruthenium, please refer to the corresponding resources.
Services
Ruthenium Products & Solutions
Precious Metal Compounds & Homogeneous Catalysts
Heterogeneous Catalysts
Precious Coatings
Hydrogen Systems
Antimicrobial Technology
More Categories